Linux 性能测试实践
前言
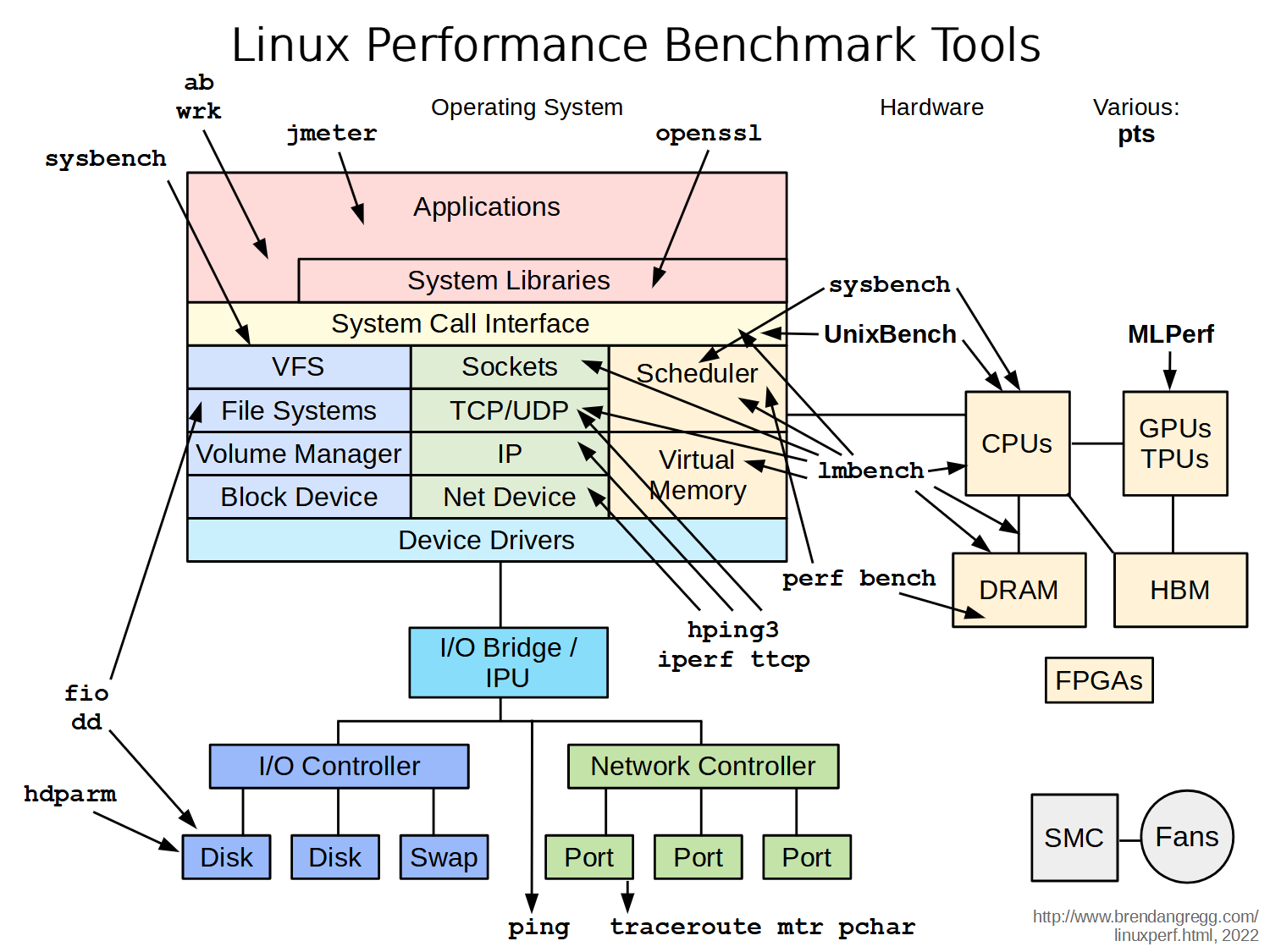
Linux 性能测试、监控、优化是一个持续的过程,上图为 LinuxCon 上 Brendan D. Gregg 分享的 Linux benchmarking tools 示意图,涵盖面十分广泛。我们可以通过成熟的监控方案如 BMC Patrol,Zabbix 来捕获大部分信息,在实际工作中我们会经常关注 I/O 性能,一般可以使用 dd/ORION/IOzone 做简单的测试,如果需要获取更加全面详细的报告可以使用 nmon,本文将主要介绍 Super PI /dd/nmon 三种简单而有效的监测方法。
CPU | Memory | I/O | Network 一个都不能少
更新记录
2015 年 03 月 06 日 - 初稿
阅读原文 - https://liaojiaxin158.github.io/post/linux-performance/
扩展阅读
- Linux Performance - http://www.brendangregg.com/linuxperf.html
- AIX 下磁盘 I/O 性能分析 - http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/aix/library/1203_weixy_aixio/
- nmon - http://nmon.sourceforge.net/pmwiki.php
CPU
确认 CPU 型号
1 | cat /proc/cpuinfo |grep "model name"|uniq|cut -f2 -d: |
Super PI
计算时间越短越好
1 |
|
Disk
清空缓存
每次做读写测试前建议先清空缓存
sync; echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
测试读性能
选择测试磁盘,建议做 2-3 组取平均值
hdparm -t /dev/sda
/dev/sda:
Timing buffered disk reads: 1074 MB in 3.00 seconds = 357.92 MB/sec
测试写入性能
根据业务选择不同的 BlockSize 大小按需多次测试取平均值
time dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/speed bs=1M count=2K conv=fsync;rm /tmp/speed
参考数据
以 10,000 rpm 300 GB SAS 硬盘为例,机型为 IBM x3650 M4,Raid 参数如下
1.Read Policy:Ahead (控制器缓存读策略:预读)
2.Write Policy:Write Back with BBU(控制器缓存写策略:有电池备份时回写)
3.IO Policy: Direct(IO 策略:直接)
4.Drive Cache:disable (硬盘缓存:禁用)
| Raid | Read(MB) | Write(MB) |
|---|---|---|
| Raid 1 | 170 | 130 |
| Raid 5 | 350 | 250 |
| Raid 10 | 300 | 215 |
nmon
建议根据实际需求配置间隔时间和次数,配合
nmon Analyser可以显示直观的图表数据
#author: OX
#function: monitor system information
#time:2015/03/06
#crontab -e
#0 0 * * * sh /tmp/nmon/nmon.sh >/dev/null 2>&1
npath=/tmp/nmon/log
# monitoring per 120 senonds
#nmon -s 120 -c 720 -f -m $npath
# monitoring per 300 senonds
/tmp/nmon/nmon_x86_sles11 -s 300 -c 288 -f -m $npath
#delete file before 365 day
#find /tmp -name *.nmon -mtime +365 -exec rm {} \;